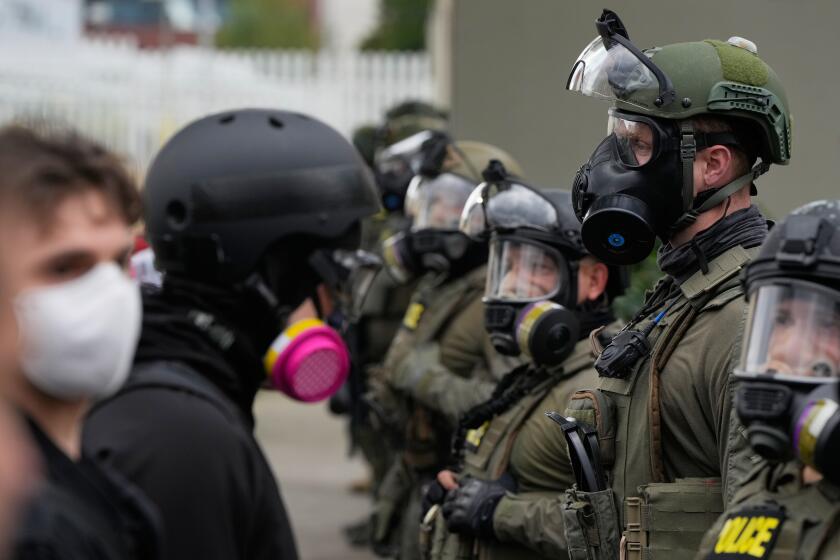
President Trump has often locked horns with the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals, with the once left-leaning court putting a persistent drag on his first-term agenda.
And now, even after remaking the bench with his own appointees, the president is still tangling with the West Coast’s federal appellate court — a situation poised to boil over as the circuit juggles multiple challenges to his use of the National Guard to police American streets.
“I appointed the judge and he goes like that — I wasn’t served well,” Trump told reporters Sunday, lashing out at U.S. District Judge Karin Immergut of Portland after she temporarily blocked the deployment federalized troops.
“To have a judge like that, that judge ought to be ashamed of himself,” Trump said, referring to Immergut, who is a woman.
The president has long railed against judges who rule against him, calling them “monsters,” “deranged,” and “radical” at various points in the past.
Trump has also occasionally sniped at conservative jurists, including U.S. Supreme Court Chief Justice John Roberts, whom he called “disgraceful” after the court rejected his bid to overturn the 2020 election.
But this weekend’s spat marked a shift in his willingness to go after his own appointees — a turn experts say could become much sharper as his picks to the appellate bench test his ambition to put boots on the ground in major cities across the U.S.
“The fact that a pretty conservative judge ruled the way she did is an indication that some conservative judges would rule similarly,” said Ilya Somin, a law professor at George Mason University and a constitutional scholar at the Cato Institute.
The 9th Circuit handed the administration an early victory in the troop fight this spring, finding that courts must give “a great level of deference” to the president to decide whether facts on the ground warrant military intervention.
That ruling is set to be reviewed by a larger appellate panel, and could ultimately be reversed. The circuit is also now set to review a September decision barring federalized troops in California from aiding in civilian law enforcement, as well as Immergut’s temporary restraining order blocking the deployment over the weekend.
In the meantime, the 9th Circuit’s June decision has served as a guidepost for states seeking to limit what Oregon called a “nationwide campaign to assimilate the military into civilian law enforcement.”
“That decision is binding, and it does require a substantial degree of deference on the factual issues,” Somin said. “[But] when what the president does is totally divorced from reality, that limit is breached.”
Immergut appeared to agree, saying in her ruling that circumstances in Portland this fall were significantly different than those in L.A. in the spring. While some earlier protests did turn violent, she wrote, recent pickets outside Portland’s ICE headquarters have featured lawn chairs and low energy.
“Violence elsewhere cannot support troop deployments here, and concern about hypothetical future conduct does not demonstrate a present inability to execute the laws using nonmilitary federal law enforcement,” the judge wrote, addressing the 9th Circuit decision.
“The President is certainly entitled ‘a great level of deference,’” Immergut continued. “But ‘a great level of deference’ is not equivalent to ignoring the facts on the ground. … The President’s determination was simply untethered to the facts.”
But exactly where the appellate court may draw the line on presidential fact-finding is tricky, experts said.
“How much deference is owed to the president? That’s something we’re all talking about,” said John C. Dehn, a professor at Loyola University Chicago School of Law.
Whether courts can review the president’s judgment at all is a matter that splits even some of the president’s most conservative judicial picks from his current justice department attorneys.
So far, Trump has relied on an esoteric subsection of the U.S. Code for the authority to send soldiers on immigration raids and to control crowds of protesters.
Dehn and others have characterized that reading of the code as semantic and divorced from its legal context.
“They’re looking at the words in a vacuum and arguing the broadest possible meaning they could can think of,” Dehn said. “The administration is not engaged in good faith statutory interpretation — they’re engaged in linguistic manipulation of these statues.”
Immegur agreed, quoting Supreme Court precedent saying “[i]nterpretation of a word or phrase depends upon reading the whole statutory text.”
For some conservative legal scholars, Trump appointees’ willingness to push back on repeated deployments could signal a limit — or a dangerous new escalation in the administration’s attacks on jurists who defy them.
“It’s obvious the administration is trying to do this on a bigger scale,” Somin said. “Ideally we would not rely on litigation alone to deal with it.”
This story originally appeared in Los Angeles Times.