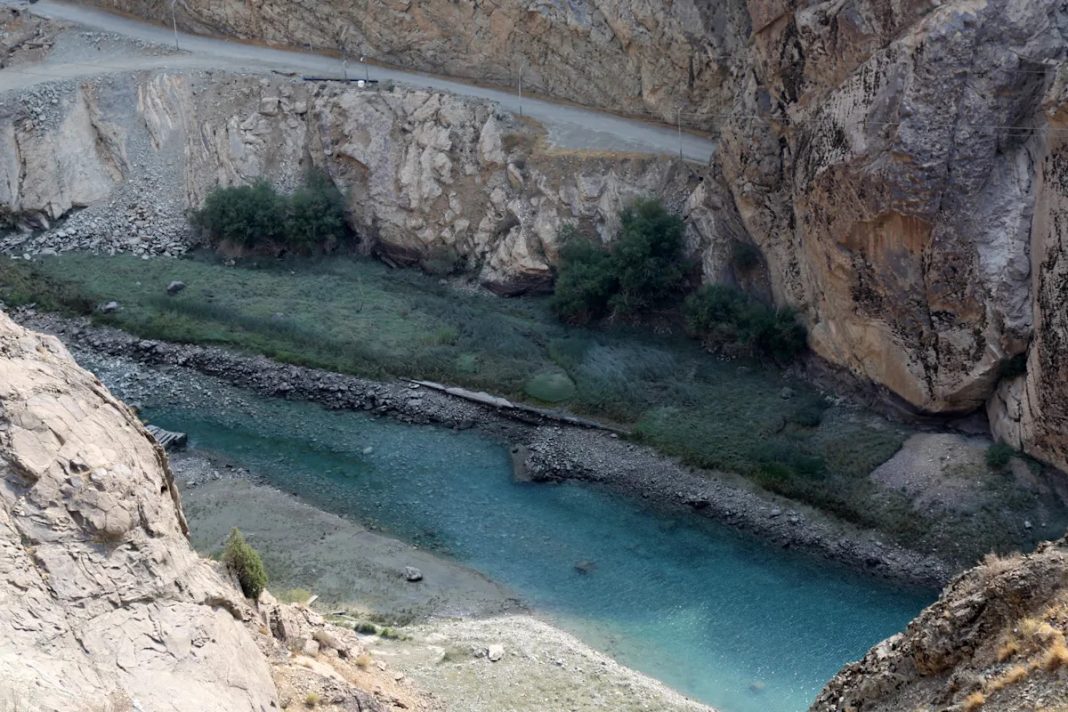
The main source of drinking water for residents of the Iranian capital Tehran is at risk of running dry within two weeks, according to state media, due to a historic drought plaguing the country.
The Amir Kabir Dam, one of five that provide drinking water for Tehran, “holds just 14 million cubic metres of water, which is eight percent of its capacity”, the director of the capital’s water company, Behzad Parsa, was quoted as saying by the IRNA news agency on Sunday.
At that level, it can only continue to supply Tehran with water “for two weeks”, he warned.
The announcement comes as the country experiences its worst drought in decades. The level of rainfall in Tehran province was “nearly without precedent for a century”, a local official declared last month.
The megacity of more than 10 million people is nestled against the southern slopes of the often snow-capped Alborz Mountains, which soar as high as 5,600 metres (18,370 feet) and whose rivers feed multiple reservoirs.
A year ago, the Amir Kabir dam held back 86 million cubic metres of water, Parsa said, but there had been a “100 percent drop in precipitation” in the Tehran region.
Parsa did not provide details on the status of the other reservoirs in the system.
According to Iranian media, the population of Tehran consumes around three million cubic metres of water each day.
As a water-saving measure, supplies have reportedly been cut off to several neighbourhoods in recent days, while outages were frequent this summer.
In July and August, two public holidays were declared to save water and energy, with power cuts an almost daily occurrence amid a heatwave that saw temperatures rise beyond 40 Celsius (104 Fahrenheit) in Tehran and exceed 50C (122F) in some areas.
“The water crisis is more serious than what is being discussed today,” Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian warned at the time.
Water scarcity is a major issue throughout Iran, particularly in arid provinces in the country’s south, with shortages blamed on mismanagement and overexploitation of underground resources, as well as the growing impact of climate change.
Iran’s neighbour Iraq is experiencing its driest year on record since 1993, as the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, which flow into the Persian Gulf from West Asia, have seen their levels drop by up to 27 percent due to poor rainfall and upstream water restrictions, leading to a severe humanitarian crisis in the country’s south.