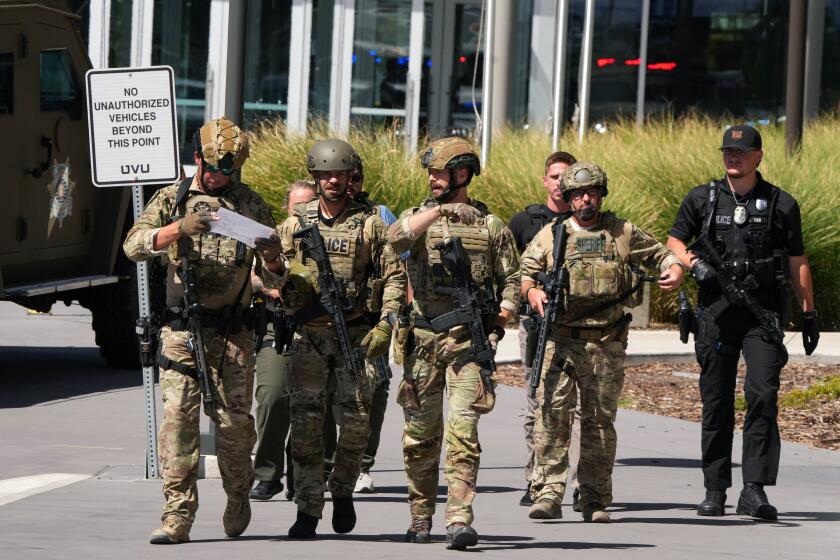
Two assassination attempts on President Trump. The assassination of a Minnesota state lawmaker and her husband and the wounding of others. The assassination of a top healthcare executive. The killing of two Israeli embassy employees in Washington. The storming of the U.S. Capitol by a violent mob intent on forcing the nation’s political leaders to their will.
And, on Wednesday, the fatal shooting of one of the nation’s most prominent conservative political activists — close Trump ally Charlie Kirk — as he spoke at a public event on a university campus.
If it wasn’t already clear from all those other incidents, Kirk’s killing put it in sharp relief: The U.S. is in a new era of political violence, one that is starker and more visceral than any other in decades — perhaps, experts said, since the fraught days of 1968, when two of the most prominent figures in the civil rights movement, the Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. and Robert F. Kennedy, were both assassinated in a matter of months.
“We’re very clearly in a moment where the temperature of our political discourse is extremely high,” said Ruth Braunstein, an associate professor of sociology at Johns Hopkins University who has studied religion and the far right in modern politics. “Part of what we see when that happens are these outbursts of political violence — where people come to believe that violence is the only solution.”
While the exact motives of the person who shot Kirk are still unknown, Braunstein and other experts on political violence said the factors shaping the current moment are clear — and similar to those that shaped past periods of political violence.
Read more: Chabria: Charlie Kirk’s killing is horrific — and likely not the end of political violence
Intense economic discomfort and inequity. Sharp divisions between political camps. Hyperbolic political rhetoric. Political leaders who lack civility and constantly work to demonize their opponents. A democratic system that many see as broken, and a hopelessness about where things are headed.
“There are these moments of great democratic despair, and we don’t think the political system is sufficiently responsive, sufficiently legitimate, sufficiently attentive, and that’s certainly going on in this particular moment,” said Jon Michaels, a UCLA law professor who teaches about the separation of powers and co-authored “Vigilante Nation: How State-Sponsored Terror Threatens Our Democracy.”
“If we think there are no political solutions, there are no legal solutions, people are going to resort to forms of self help that are really, really deeply troubling.”
Michaels said the country has been here before, but also that he worries such cycles of violence are occurring faster today and with shorter breaks in between — that while “we’ve been bitterly divided” for years, those divisions have now “completely left the arena of ideas and debate and contestation, and become much more kinetic.”
Michaels said he is still shaken by all the “defenses or explanations or rationalizations” that swirled around the country after the killing of UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson in New York City in December — which some people argued was somehow justified by their displeasure with UnitedHealthcare’s policies or frustration with the American healthcare system.
That the suspect, Luigi Mangione, would attract almost cult-like adoration in some circles seemed like an alarming shift in an already polarized nation, Michaels said.
“I understand it is not the beliefs of the typical person walking down the street, but it’s seeping into our culture slowly but surely,” he said — and in a way that makes him wonder, “Where are we going to be in four or five years?”
People across America were asking similar questions about Wednesday’s shooting, wondering in which direction it might thrust the nation’s political discourse in the days ahead.
How will Kirk’s many conservative fans — including legions of young people — respond? How will leaders, including Trump, react? Will there be a shared recognition that such violence does no good, or fresh attempts at retaliation and violence?
Leaders from both parties seemed interested in averting the latter. One after another, they denounced political violence and defended Kirk’s right — everyone’s right — to speak on politics in safety, regardless of whether their message is uplifting or odious.
Democrats were particularly effusive in their denunciations, with Gov. Gavin Newsom — a chief Trump antagonist — calling the shooting “disgusting, vile, and reprehensible.” Former President Obama also weighed in, writing, “We don’t yet know what motivated the person who shot and killed Charlie Kirk, but this kind of despicable violence has no place in our democracy.”
Many seemed dismissive of such messages. In the comments on Obama’s post, many blamed Obama and other Democrats for rhetoric demonizing Republicans — and Trump and his followers in particular — as Nazis or racists or fascists, suggesting that the violence against Kirk was a predictable outcome of such pitched condemnations.
Trump echoed those thoughts himself Wednesday night, blaming the “radical left” for disparaging Kirk and other conservatives and bringing on such violence.
Others seemed to celebrate Kirk’s killing or suggest it was justified in some way given his own hyperbolic remarks from the past. They dug up interviews where the conservative provocateur demonized those on the left, suggested liberal ideas constituted a threat to Western civilization, and even said that some gun violence in the country was “worth it” if it meant the freedom to bear arms.
Experts said it is important to contextualize this moment within American history, but with an awareness of the modern factors shaping it in unique ways. It’s also important to understand that there are ways to combat such violence from spreading, they said.
Peter Mancall, a history professor at USC, has delved into major moments of political violence in early American history, and said a lot of it stemmed from “some perception of grievance.”
The same appears to be true today, he said. “There are moments when people do things that they know are violating their own sense of right or wrong, and something has pushed them to it, ” he said. “The trick is figuring out what it is that made them snap.”
Braunstein said that the robust debate online Wednesday about the rhetoric of leaders was a legitimate one to have, because it has always been true that “the way our political leaders message about political violence — consistently, in public, to their followers and to those that don’t support them — really matters.”
If Americans and American political leaders truly want to know how we got here, she said, “part of the answer is the intensification of violent political rhetoric — and political rhetoric that casts the moment in terms of an emergency or catastrophe that requires extreme measures to address it.”
Democrats today are talking about the threats they believe Trump poses to democracy and the rule of law and to immigrants and LGBTQ+ people and others in extremely dire terms. Republicans — including Kirk — have used similarly charged rhetoric to suggest that Democrats and some of those same groups, especially immigrants, are a grave threat to average Americans.
“Charlie Kirk was one of many political figures who used that kind of discourse to mobilize people,” Braunstein said. “He’s not the only one, but he regularly spoke about the fact that we were in a moment where it was possible that we were going to see the decline of Western civilization, the end of American society as we know it. He used very strong us-vs.-them language.”
Particularly given the wave of recent violence, it will be important moving forward for politicians and other leaders to reanalyze how they speak about their political disagreements, Braunstein said.
That’s especially true of Trump, she said, because “one of the most dangerous things that can happen in a moment like this is for a political leader to call for violence in response to an act of violence,” and Trump has appeared to stoke violence in the past, including on Jan. 6, 2021, at the Capitol and during racist marches through Charlottesville, Va., in 2017.
Charlie Kirk speaks during a town hall meeting in March in Oconomowoc, Wis. (Jeffrey Phelps / Associated Press)
Dr. Garen Wintemute, director of the Centers for Violence Prevention at UC Davis, agreed messaging is key — not just for responding to political violence, but for preventing it.
Since 2022, Wintemute and his team have surveyed Americans on how they feel about political violence, including whether it is ever justified and, if so, whether they would personally get involved in it.
Throughout that time frame, a strong majority of Americans — about two-thirds — have said it is not justified, with about a third saying it was or could be.
Read more: Charlie Kirk was a force with young conservatives, boosting GOP and Trump
An even smaller minority said they’d be willing to personally engage in such violence, Wintemute said. And many of those people said that they could be dissuaded from participating if their family members, friends, religious or political leaders urged them not to.
Wintemute said the data give him “room for hope and optimism,” because they show that “the vast majority of Americans reject political violence altogether.”
“So when somebody on a day like today asks, ‘Is this who we are?’ we know the answer,” he said. “The answer is, ‘No!'”
The job of all Americans now is to reject political violence “out loud over and over and over again,” Wintemute said, and to realize that, if they are deeply opposed to political policies or the Trump administration and “looking for a model of how to resist,” it isn’t the American Revolution but the civil rights movement.
“People did not paint over how terrible things were,” he said. “People said, ‘I will resist, but I will resist without violence. Violence may be done to me, I may die, but I will not use violence.'”
This story originally appeared in Los Angeles Times.