LA PAZ, Bolivia (AP) — Bolivians headed to the polls on Sunday to elect a new president and parliament in elections that could spell the end of the Andean nation’s long-dominant leftist party and see a right-wing government elected for the first time in over two decades.
The vote is one of the most consequential for Bolivia in recent times — and one of the most unpredictable.
Even at this late stage, a remarkable 30% or so of voters remain undecided. Polls have shown the two leading right-wing candidates, multimillionaire business owner Samuel Doria Medina and former President Jorge Fernando “Tuto” Quiroga, locked in a virtual dead heat.
Many undecided voters
A right-wing victory isn’t assured. Many longtime voters for the governing Movement Toward Socialism, or MAS, party, now shattered by infighting, live in rural areas and tend to be undercounted in polling.
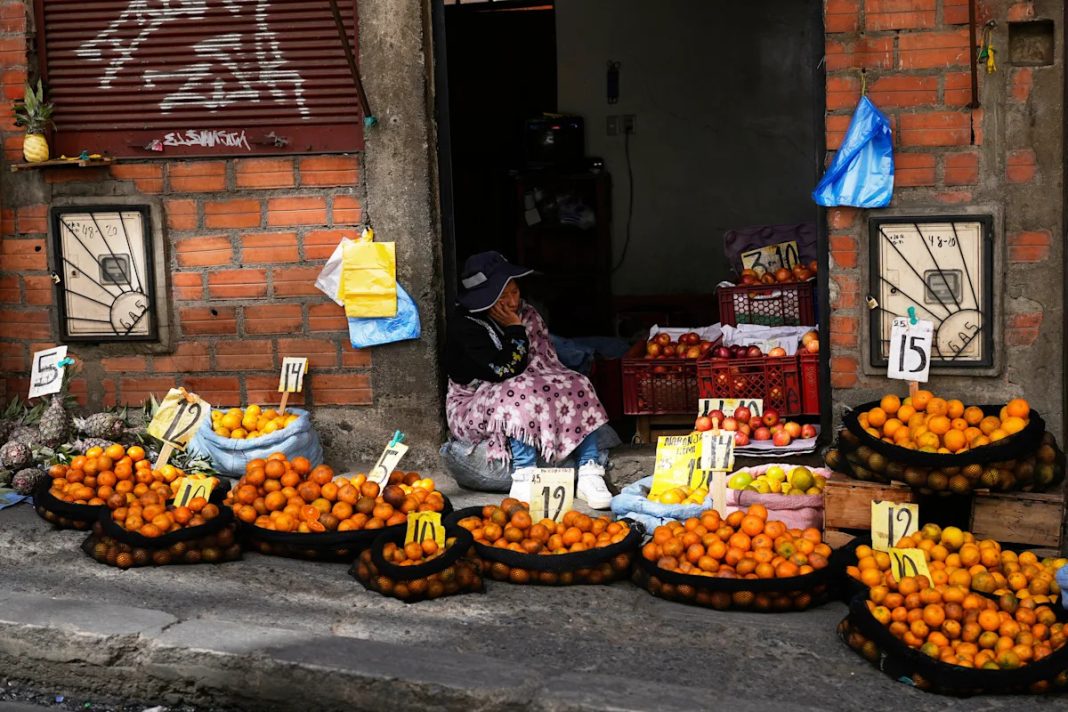
With the nation’s worst economic crisis in four decades leaving Bolivians waiting hours in fuel lines, struggling to find subsidized bread and squeezed by double-digit inflation, the opposition candidates bill the race as a chance to alter the country’s destiny.
“I have rarely, if ever, seen a situational tinderbox with as many sparks ready to ignite,” said Daniel Lansberg-Rodriguez, founding partner of Aurora Macro Strategies, a New York-based advisory firm.
Bolivia could follow rightward trend
The outcome will determine whether Bolivia — a nation of about 12 million people with the largest lithium reserves on Earth and crucial deposits of rare earth minerals — follows a growing trend in Latin America, where right-wing leaders like Argentina’s libertarian Javier Milei, Ecuador’s strongman Daniel Noboa and El Salvador’s conservative populist Nayib Bukele have surged in popularity.
A right-wing government in Bolivia could trigger a major geopolitical realignment for a country now allied with Venezuela’s socialist-inspired government and world powers such as China, Russia and Iran.
Right-wing candidates vow to restore US relations
Doria Medina and Quiroga have praised the Trump administration and vowed to restore ties with the United States — ruptured in 2008 when charismatic, long-serving former President Evo Morales expelled the American ambassador.
The front-runners also have expressed interest in doing business with Israel, which has no diplomatic relations with Bolivia, and called for foreign private companies to invest in the country and develop its rich natural resources.
After storming to office in 2006 at the start of the commodities boom, Morales, Bolivia’s first Indigenous president, nationalized the nation’s oil and gas industry, using the lush profits to reduce poverty, expand infrastructure and improve the lives of the rural poor.
After three consecutive presidential terms, as well as a contentious bid for an unprecedented fourth in 2019 that set off popular unrest and led to his ouster, Morales has been barred from this race by Bolivia’s constitutional court.
His ally-turned-rival, President Luis Arce, withdrew his candidacy for the MAS on account of his plummeting popularity and nominated his senior minister, Eduardo del Castillo.
As the party splintered, Andrónico Rodríguez, the 36-year-old president of the senate who hails from the same union of coca farmers as Morales, launched his bid.
Ex-president Morales urges supporters to deface ballots
Rather than back the candidate widely considered his heir, Morales, holed up in his tropical stronghold and evading an arrest warrant on charges related to his relationship with a 15-year-old girl, has urged his supporters to deface their ballots or leave them blank.
Voting is mandatory in Bolivia, where some 7.9 million Bolivians are eligible to vote. President Arce appealed to the population to reject Morales’ calls, arguing that those spoiling their ballots were doing damage to democracy.
“We urge the population to go out and vote,” he said while casting his vote in Bolivia’s capital of La Paz. “We must demonstrate unity and commitment to democracy.”
Doria Medina and Quiroga, familiar faces in Bolivian politics who both served in past neoliberal governments and have run for president three times before, are struggling to stir up interest as voter angst runs high.
“There’s enthusiasm for change but no enthusiasm for the candidates,” said Eddy Abasto, 44, a Tupperware vendor in La Paz torn between voting for Doria Medina and Quiroga. “It’s always the same, those in power live happily spending the country’s money, and we suffer.”
Conservative candidates say austerity needed
Whoever wins faces daunting challenges. Doria Medina and Quiroga have warned of the need for a painful fiscal adjustment, including the elimination of Bolivia’s generous food and fuel subsidies, to save the nation from insolvency.
Some analysts caution this risks sparking social unrest.
“A victory for either right-wing candidate could have grave repercussions for Bolivia’s Indigenous and impoverished communities,” said Kathryn Ledebur, director of the Andean Information Network, a Bolivian research group.
“Both candidates could bolster security forces and right-wing para-state groups, paving the way for violent crackdowns on protests expected to erupt over the foreign exploitation of lithium and drastic austerity measures.”
All 130 seats in Bolivia’s Chamber of Deputies, the lower house of Parliament, are up for grabs, along with 36 in the Senate, the upper house.
If, as is widely expected, no one receives more than 50% of the vote, or 40% of the vote with a lead of 10 percentage points, the top two candidates will compete in a runoff on Oct. 19 for the first time since Bolivia’s 1982 return to democracy.