NEW YORK (AP) — Researchers on Wednesday reported two promising new approaches to counteract malaria’s growing resistance to medication — one involving a new class of drugs.
Switzerland-based Novartis released results of what it called a next-generation treatment. A study of its experimental drug in 12 African countries found it works well against the mosquito-borne parasite that causes malaria and seems to block spread.
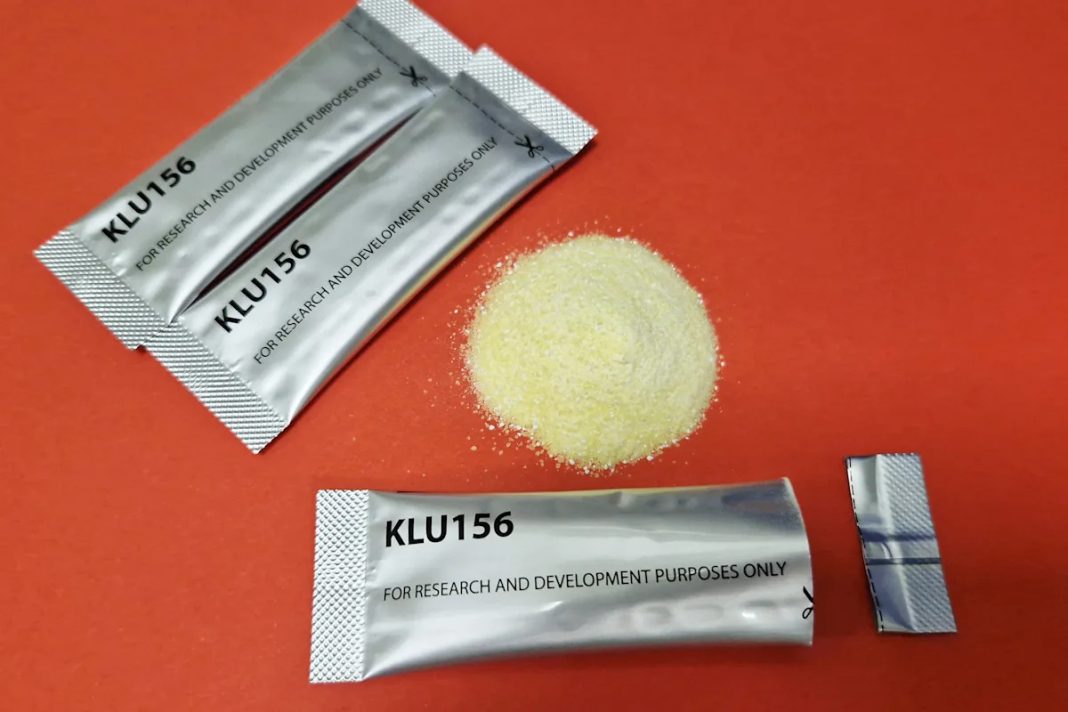
The drug, called GanLum, is not yet licensed and more than a year away from being available.
It’s needed, said Dr. David Sullivan, a malaria expert at Johns Hopkins University.
The parasite that causes the disease is developing resistance to existing drugs, meaning “the ice is thinning,” Sullivan said. “It hasn’t given way, but we’re concerned.”
GanLum has been given as a packet of tiny powder-like granules, once daily for three days. But getting people to take malaria drugs over several days has been challenging — some stop after one or two doses makes them feel better. Experts say a third or more of malaria patients fail to complete the current standard three-day treatment course, a problem that can encourage drug resistance and allow curable cases to intensify.
In an effort to offer a one-time treatment, another team of researchers said an experiment in West Africa found a single dose of four widely available malaria drugs proved to be an effective cure.
The two studies were presented Wednesday at the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene conference in Toronto.
Parasite has repeatedly developed drug resistance
Malaria is caused by a parasite that spreads through mosquito bites. Infected people can suffer fever, chills and flu-like illness that, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications and death. It’s mainly found in tropical and subtropical climates. The largest death toll in recent years has been seen in children in sub-Saharan Africa.
The medical battle against malaria has ebbed and flowed, as new drugs come along, but the parasite gradually develops the ability to resist them.
At the beginning of this century, for example, resistance to the drug chloroquine was widespread and malaria killed more than 1.8 million people per year. But then came a class of drugs known as artemisinins, which worked well and helped drive a dramatic decline in global malaria death rates.
Artemisinin-based compounds remain the first-line treatment in most cases. But signs of partial resistance have been reported, and — for several reasons — malaria death rates have plateaued or even started to rise in some parts of the world.
Study tested 4-drug combo
Dr. Ghyslain Mombo-Ngoma led a study in Gabon in which researchers gave a single-dose treatment combining an artemisinin with three other antimalarial medications — pyronaridine, sulfadoxine, and pyrimethamine.
From May 2024 to October 2025, he and his colleagues treated more than 1,000 patients, half of them younger than 10, who were sick with malaria but not suffering life-threatening symptoms. A little over half got the four-drug, one-time treatment. The rest got a standard, artemisinin-based treatment.
Blood tests 28 days later showed 93% of patients who received the one-time treatment were free of parasites compared with 90% who received the standard three-day course.
Mombo-Ngoma said there are discussions underway with a drug manufacturer to produce a single capsule or packet of pills to help create an inexpensive, easy-to-take cure.
Sullivan, however, noted that resistance is already established to some components of the treatment, meaning it likely will prove to be “a short-term fix.”
Experimental treatment shows promise
Novartis’ GanLum is a combination of a new drug, ganaplacide, and an existing long-acting medication, lumefantrine.
In a study involving about 1,700 adults and children in 12 African countries, GanLum was found to have a cure rate of better than 97%, which was a little higher than a common artemisinin-based treatment. It was also highly effective against mutant malaria parasites with partial drug resistance, Novartis officials said.
Side effects included fever and anemia — similar to what’s seen in patients who take some of the current antimalarials, Novartis officials said. There was a higher level of vomiting right after the drug was given, which company officials say may stem from its taste. The company is exploring flavoring or sweetening, a spokesman said.
Novartis officials said they are working toward regulatory approvals. George Jagoe of the Medicines for Malaria Venture, which collaborated with Novartis, said he hopes to see GanLum begin rolling out to patients within 18 months.
The new treatment approaches can complement other efforts against malaria, including treated mosquito bed nets and new vaccines, said Dr. Andrea Bosman, a malaria expert with the World Health Organization.
But the promising news comes at a time when funding from the United States and some other sources is being cut, which could impact the ability of scientists to monitor drug resistance or make prevention and treatments available to people who need them, Bosman noted.
“The eyes on the problem are going to be blinded” as aid to malaria-stricken countries declines, he said.
___
The Associated Press receives financial support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the Gates Foundation, among others. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.